Keeping your vehicle running smoothly requires attention to various components, but few are as critical as the timing belt. This unassuming piece of reinforced rubber plays a pivotal role in your engine’s operation and deserves special consideration in your maintenance routine. Neglecting it could lead to costly repairs or even complete engine failure. Let’s explore how proper timing belt maintenance can ensure optimal performance for your motor.
Understanding your timing belt’s role
The timing belt, also known as a cambelt in many automotive circles, serves as the crucial link between your engine’s crankshaft and camshaft. This synchronisation ensures that the engine’s valves open and close at precisely the right moments during the combustion process. Without this perfect timing, your engine simply cannot function properly. Many vehicle owners visiting https://www.motorpublish.it/ often discover that understanding this component’s function helps them appreciate why its maintenance cannot be overlooked.
How timing belts affect engine synchronisation
The timing belt’s primary job is maintaining perfect harmony between the crankshaft and camshaft operations. When these two components are properly synchronised, the engine valves open and close at exactly the right moment in relation to the pistons’ movement. This precision allows for optimal fuel combustion, efficient power delivery, and smooth operation. Made of reinforced rubber designed to withstand high temperatures and constant use, the timing belt must remain intact and properly tensioned at all times. If synchronisation fails due to belt issues, the engine’s performance will deteriorate rapidly, potentially causing catastrophic damage.
Signs of a deteriorating timing belt
Recognising the warnings of a failing timing belt can save you from serious engine damage and expensive repairs. Common symptoms include unusual ticking or squealing noises coming from the engine area, which often indicate the belt is loose or wearing unevenly. You might also notice rough idling when your car is stationary, or the engine misfiring during operation. More severe symptoms include the engine refusing to start altogether or significant loss of power during acceleration. Oil leaks near the timing belt area can also signal problems, as they might indicate failing seals or gaskets associated with the timing system. These warning signs should never be ignored, as complete belt failure while driving can leave you stranded and facing a much costlier repair bill.
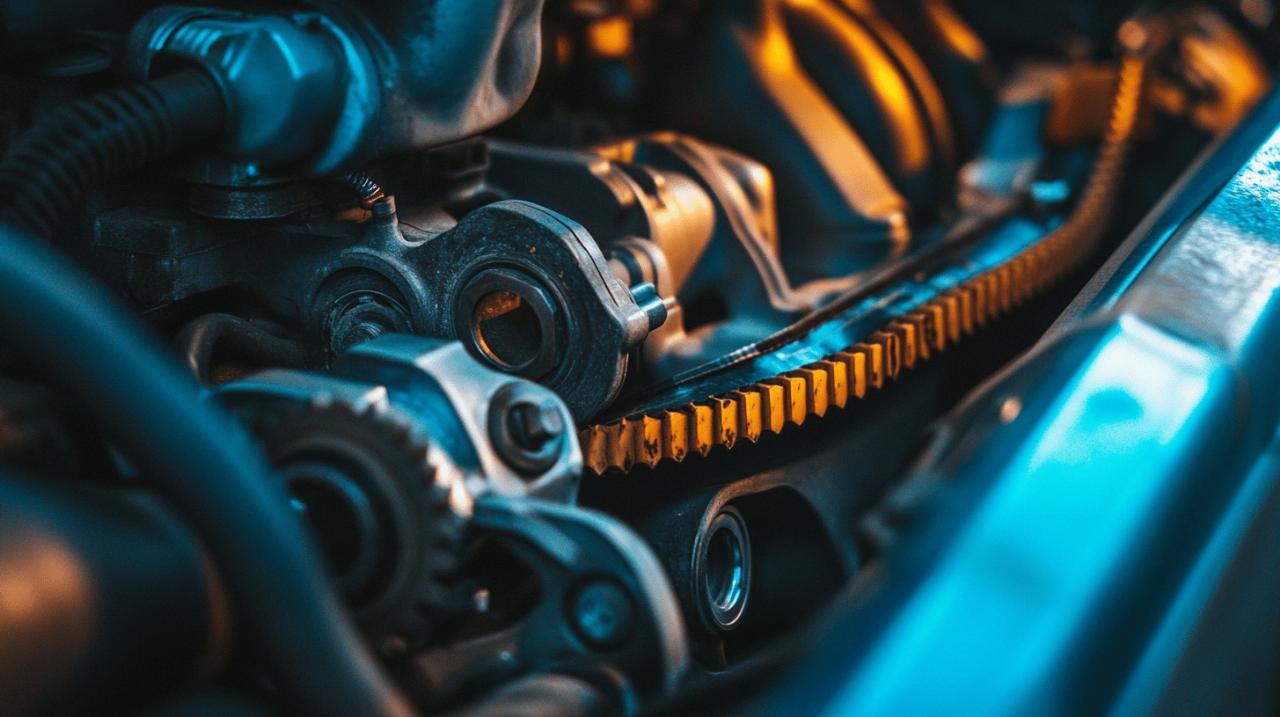
Proper maintenance schedules for longevity
Adhering to manufacturer-recommended maintenance intervals is perhaps the most important aspect of timing belt care. Unlike other components that might give obvious warnings before failing, a timing belt can appear fine right up until the moment it breaks. This unpredictability makes preventative maintenance absolutely essential for avoiding serious engine damage. Most automotive experts agree that replacing this critical component before it fails is significantly less expensive than addressing the aftermath of a broken belt.
Manufacturer recommendations for replacement intervals
Different car brands have varying guidelines for timing belt replacement, but most fall within similar ranges. Volkswagen typically recommends replacement every 60,000 to 90,000 miles, with costs ranging from £400 to £900. Toyota and Ford both suggest intervals of 60,000 to 100,000 miles, with Toyota replacements costing between £300 and £800, and Ford services ranging from £300 to £700. Honda owners should consider replacement every 60,000 to 100,000 miles or every 7 years, whichever comes first, with costs between £400 and £900. Luxury brands like Audi and BMW generally recommend changes at 75,000 to 100,000 miles and 60,000 to 100,000 miles respectively, with higher service costs ranging from £400 to £1,200. Regardless of make, consulting your specific vehicle’s manual for the exact recommendation is always the safest approach.
Factors that accelerate timing belt wear
Several conditions can cause your timing belt to deteriorate faster than expected. Extreme temperature fluctuations place additional stress on the rubber material, causing it to expand and contract repeatedly. Frequent short trips prevent your engine from reaching optimal operating temperature, which can accelerate wear on all components, including the timing belt. Oil or coolant leaks can contaminate the belt material, breaking down its structural integrity over time. Improper tension during installation can cause premature wear, whether the belt is too tight or too loose. Environmental factors also play a role, with vehicles operated in particularly dusty, humid, or corrosive environments requiring more frequent inspections and potentially earlier replacements. When replacing the timing belt, many mechanics recommend simultaneously replacing the water pump if it’s driven by the same belt, as this preventative step can save on labour costs down the line.
